GDB tutorial
Introdution
A debugger is a program that simulates /runs another program and allows you to:
-
Pause and continue its execution
-
Set “break points” or conditions where the execution pauses so you can look at its atate
-
View and “watch” variable values
-
Step through the program line-by-line(or instruction by instruction)
GDB (GNU debugger)
Compile for debugging
1
gcc -Wall -g program.c
prgoram.c is source code write in to C language
- to use gdb you’ll need to compute to program using the G flag
Start GDB
1
gdb a.out
if you requires command-line arguments you can provide them at startup using the following these can also be set inside.
1
gdb --args a.out arg1 arg2
Useful GDB commands
-
refreshg the display : refresh ( or control-L)
-
Run your program : run
-
See your code : layout next
-
Set a break point: break POINT, can be a line number, function name, etc.
-
Step: next(n for short)
-
Continue(to next break point) : continue
-
Print a variable’s value: print VARIABLE
-
Print an array: print *arr@len
-
Watch a variable for changes: watch VARIABLE
Demonstration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
/**
* This program computes the sum of the first n
* prime numbers. Optionally, it allows the user
* to provide n as a command line argument, but
* defaults to the first n = 10 primes
*/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
/**
* This function takes an integer array (of size n) and
* returns the sum of its elements. It returns 0 if the
* array is NULL or if its size is <= 0
*/
int sum(int *arr, int n);
/**
* This function returns an array containing the first
* n prime numbers
*/
int* getPrimes(int n);
/**
* This function determines returns true if the give
* integer is prime and false otherwise.
*/
int isPrime(int x);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int n = 10; //default to the first 10 primes
if(argc = 2) {
atoi(argv[2]);
}
int *primes = getPrimes(n);
int s = sum(primes, n);
printf("The sum of the first %d primes is %d\n", n, s);
return 0;
}
int sum(int *arr, int n) {
int i;
int total;
for(i=0; i<n; i++) {
total =+ arr[i];
}
return total;
}
int* getPrimes(int n) {
int result[n];
int i = 0;
int x = 2;
while(i < n) {
if(isPrime(x)) {
result[i] = x;
i++;
x += 2;
}
}
return result;
}
int isPrime(int x) {
if(x % 2 == 0) {
return 0;
}
for(int i=3; i<=sqrt(x); i+=2) {
if(x % i == 0) {
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
purpose of this program is to compute the sum of the first n prime.
optionally it allows the user to provide n as a command-line argument
but defaults to 10.
Start debugging
1
gcc -g -lm -std=c99 -w primesProgram.c
- -w for supress all the warnings
some of the warnings are going to give our bugs away immediately
which is good in practice but i want to demonstrate the debugging tool here
1
./a.out
when i run it it simply gets stuck in an infinite loop
so ahead and start up the debugger
1
gdb a.out
ctrl+x , a

there’s nothing here yet because the program is not running
so let’s start it by typing run

it is running it’s stuck in the infinite loop
if we interrupt it
using control-c
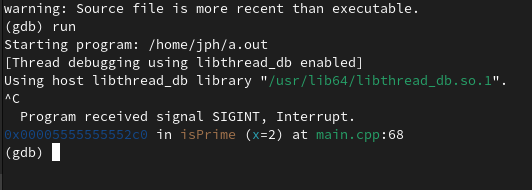
then we can see that we’re getting caught in this while loop on line 67
here I’ll go ahead and use next to step

shorthand is n
now to understand what’s going on here and why it’s getting caught in this infinite loop
let’s go ahead and print out some of these numbers i
1
print i

i is zero which it recelived on line 55
n is 10
x is 2
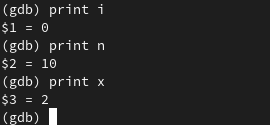
so we never get past the first iteration
clearly the problem is probably in the prime funciton.
typing next is simply going to go in this loop what I want to do is I want to go into the is prime function so instead
so instead of next i’ll type step
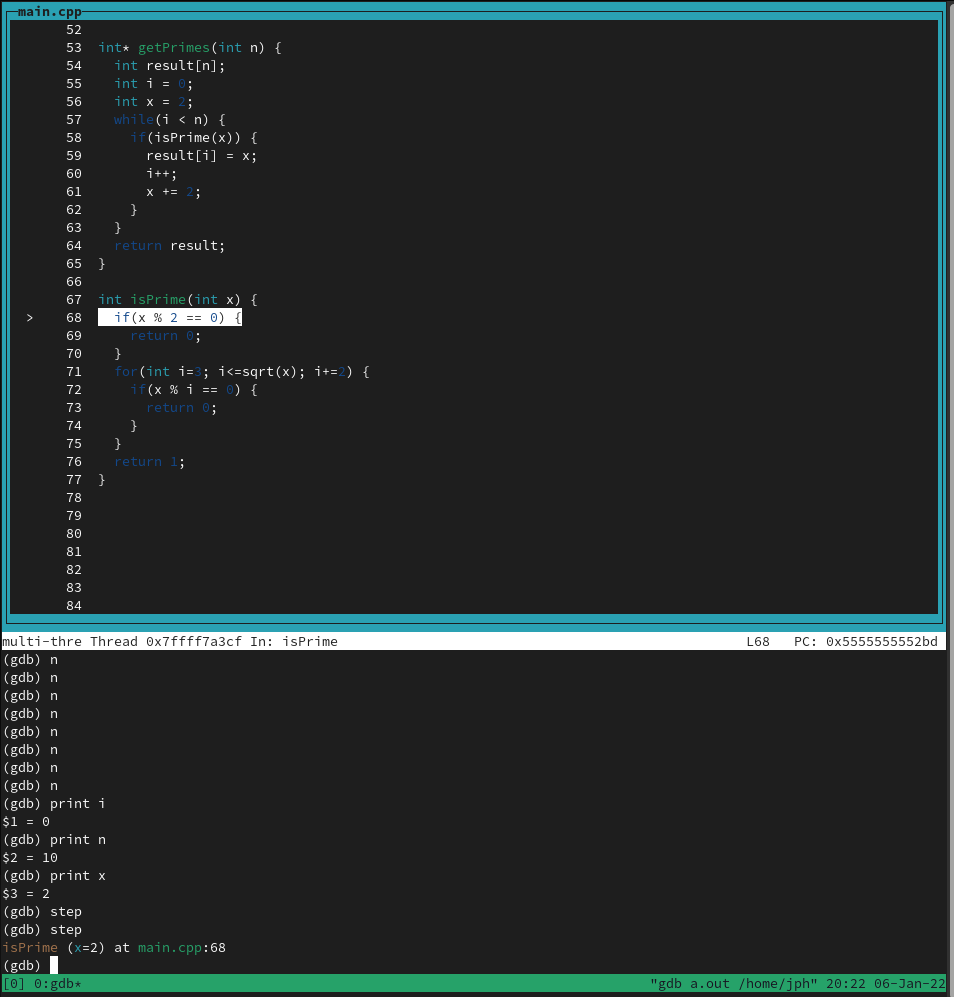
that takes me to this is prime function
the difference is that next goes to the next line in the immediate scopte
step will actually step inside of a function so you can take a look at what’s going on inside of it
1
print x
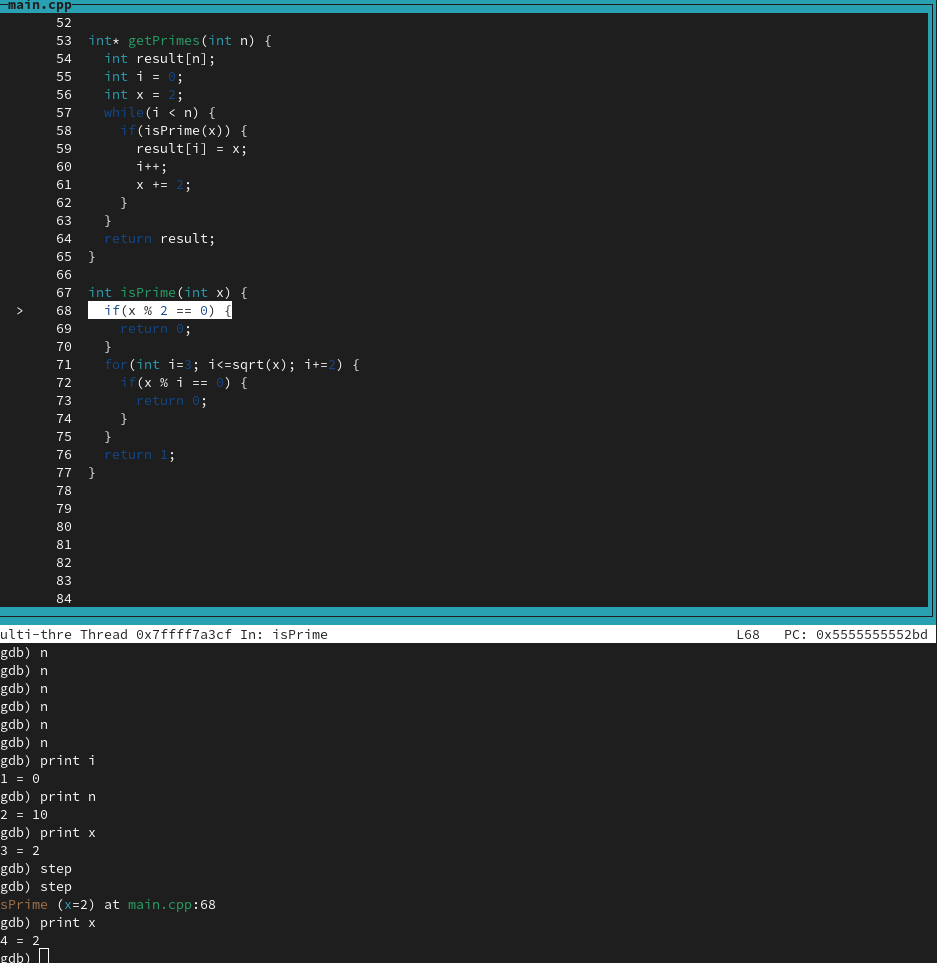
X is 2 here which is a prime number
but we’re returning false (zero)
we found our fist bug.
2 is an even number but that’s also prime .
so ket’s rethink our design here
1
quit
quit out of the debugger simply type quit
now let’s look at this a little bit closer

this function is supposed to return true if X is prime
and false otherwise
the for loop is testing whether or not X is divisible by any odd integers
starting at 3 going th 5 7 etc up until the square root of x
but one of the corner cases is when we’ve got 2
we need to return true
because 2 is a prime number
let’s take care of it with an additional conditional statement

some other corner cases that we might not have though of would be 1 , 0 or any negative numbers
which can sometimes be thought of as prime for the purposes of this program.
let’s go ahead and take care of that now
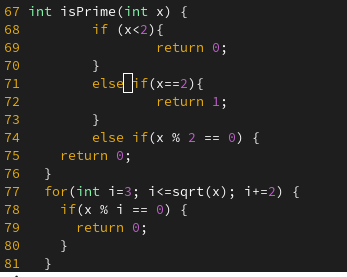
let me go ahead and recompile
1
2
g++ -g -lm -std=c99 -w primesProgram.c
./a.out
and we’re still stuck in an infinite loop
we’re still stuck here but